Cell Junctions
There are 3 functional groups of cell junctions:-
- Occluding junctions – Seal cells together in an epithelium in a way that prevents leakage of even small molecules from one cell to another
- Anchoring junctions – Mechanically attach cells (precisely, their cytoskeleton) to their neighbours or to ECM (extracellular matrix)
- Communicating junctions – Allow passage of chemicals or electrical signals from one cell to another
- Occluding Junctions
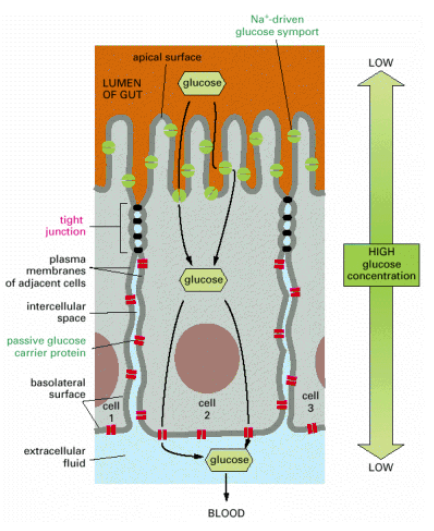
- In vertebrates, the major type of occluding junction is the tight junction in epithelial cells
- Tight junction – major protein is claudin; minor protein is occluding (they are transmembrane proteins)
- Peripheral membrane proteins called ZO proteins (Zonula Occludens) – anchors the tight junction proteins to actin of cell cortex
- In invertebrates, septate junctions are the predominant occluding junctions
- In Drosophila, the septate junctions are composed of discs large protein which is homologous to ZO protein of vertebrates
- Extracellular Ca2+ ions required for tight junction integrity
- Functions :
- Function as barriers to the diffusion of membrane proteins and lipids between apical and basolateral domains of the plasma membrane of epithelial cells in the gut lining
- Seal neighbouring cells together very tightly
- Anchoring Junctions
- Seal cells together or to ECM
- 2 types of proteins the junctions are composed of – Intracellular anchor proteins, Transmembrane adhesion protein
- 2 functional forms of anchoring junctions:
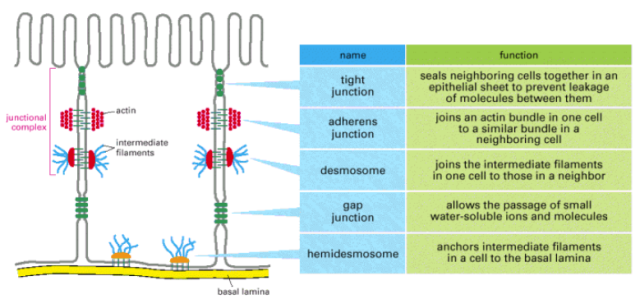
- Adherens junction & Desmosomes – Seal cells together. Transmembrane proteins involved belong to cadherin family
- Focal adhesion & Hemidesmosomes – Seal cells to ECM. Transmembrane proteins involved belong to integrin family
- Adherens junction & Focal adhesion are connected to actin filaments
- Desmosomes & Hemidesmosomes are connected to intermediate filaments
- Adherens Junctions – In epithelial cells, they form a continuous adhesion belt (zonula adherens). Intracellular anchor proteins associated – catenins (α, β, ϒ), Vinculin, α-actinin. Transmembrane adhesion proteins associated – E-cadherin. Actin filaments of the cell cortex are attached via intracellular anchor proteins to the junction proteins forming a transcellular network. Contraction by myosin helps in animal morphogenesis.
- Desmosomes – These junctions connect the intermediate filaments of adjacent cells. Intracellular anchor proteins associated – desmoplakin, plakoglobin (ϒ- catenin). Transmembrane adhesion proteins associated – desmocollin, desmoglein (cadherin family). The type of intermediate filaments involved in epithelial cells are keratin filaments and in cardiac muscles are desmin filaments. Pemphigus is an autoimmune disorder wherein the body makes antibodies to their own desmosomal cadherin proteins thereby disrupting the junctions in skin epithelium.
- Focal Adhesions – Bind muscle cells to tendons at myotendinous junctions and fibroblasts to substratum. Intracellular anchor proteins associated – talin, α-actinin, vinculin, filamin. Transmembrane adhesion proteins associated – belong to integrin family.
- Hemidesmosomes – Connects basal surface of epithelial cells to basal lamina. Intracellular anchor proteins associated – plectin, BP230. Transmembrane adhesion proteins associated – α6 β4, IN ECM, they bind laminin protein of the basal lamina. Intermediate filaments associated are keratin filaments.

- Communicating Junctions
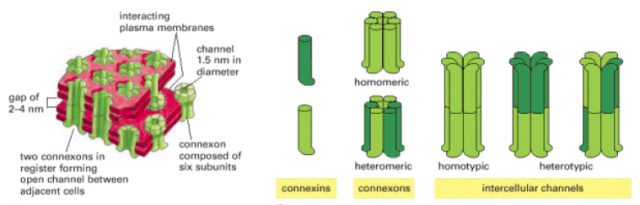
- Gap junctions are one form of communicating junctions that allow small inorganic ions and water soluble molecules to pass directly from the cytoplasm of one cell to another
- The channels are called connexons and the channel proteins are called connexins
- 6 connexins combine to form a connexon. Connexins are 4 pass transmembrane proteins
- The connexin subunits could be homomeric or heteromeric
- Functions:
- Electrical coupling in nerve cells and smooth and cardiac muscle cells. The gap junctions between these cells helps faster spread of signals through neurons and synchronizes contractions of muscle cells in heart and intestine
- In the liver, the release of noradrenaline from sympathetic nerve endings in response to a fall in blood glucose level stimulates hepatocytes to increase glycogen breakdown and release glucose into the blood. Gap junctions help the spread of the signal from the innervated cells to the non-innervated ones
- Oocyte maturation. Gap junctions between oocyte and follicular cells help transport mRNAs and various proteins to the oocyte. The type of connexin amongst the granulosa cells is Cx 43 while those between granulosa cells and oocyte is Cx 37
- The junctions mediate exchange of signal molecules that guide tissue development and the whole course of embryo development
Gap Junctions In Plants
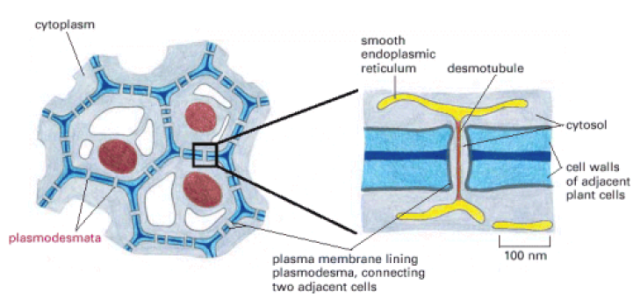
Plasmodesmata, in plants, are like gap junctions connecting cytoplasm of adjacent cells. The junctions are cylindrical channels with a diameter of 20-40 nm. Through the centre of plasmodesmata, there is a narrower cylinder called desmotubule, continuous with the elements of SER of the connected cells. Regions with dense clusters of plasmodesmata are called pit fields. They allow the passage of molecules with a molecular weight of less than about 800. During development, groups of cells within shoot and root meristems communicate through plasmodesmata. mRNAs can be passed back and forth through these junctions. Viruses can also pass from one cell to the other in this way.

good eve maam
article was really helpful and easy to understand
please post some more topics on animal physiology
thanks
richa
Hi Richa!
Thanks for reading my blog. What exactly do you want me to cover in animal physiology?